How 3D Printing Revolutionizes the Healthcare Industry
- By -Duke
- Posted on
- Posted in 3D Printers
3D printing is transforming the healthcare industry, offering solutions once deemed impossible. This innovative technology enhances patient care, reduces costs, and speeds up medical advancements. With its ability to create highly precise and customizable tools, 3D printing changes how healthcare professionals diagnose, treat, and improve lives.

Customized Medical Implants and Devices
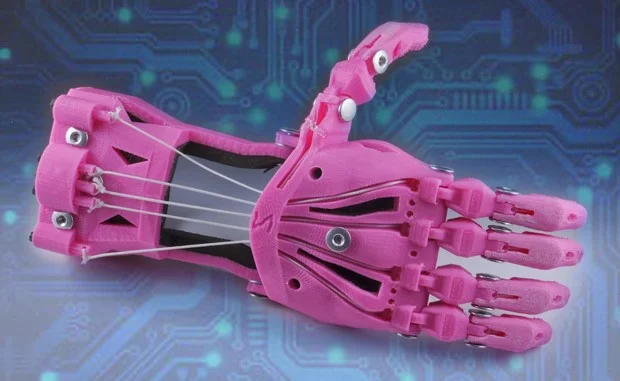
One of the most significant benefits of 3D printing in healthcare is customization. Traditional medical devices often require standard sizes, leaving some patients underserved. 3D printing changes this by producing implants and devices tailored to individual anatomy.
For instance, custom prosthetics and orthotics are now created with unmatched precision. This customization improves patient comfort and functionality. Similarly, dental professionals use 3D printing to design crowns, bridges, and aligners tailored to fit each patient perfectly.
In orthopedics, surgeons rely on 3D-printed implants for joint replacements. These implants are designed based on scans of the patient’s bones, ensuring better alignment and faster recovery.
Advancing Surgical Planning and Education
3D printing also revolutionizes surgical planning. Surgeons can print detailed models of a patient’s anatomy, including bones, organs, and blood vessels. These models help them practice and plan complex procedures before entering the operating room.
This approach enhances surgical accuracy, reduces risks, and shortens operation times. For example, in heart surgery, 3D-printed models of a patient’s heart allow doctors to visualize and address abnormalities with precision.
In medical education, 3D printing provides realistic training models. Students practice on replicas of organs and tissues, gaining hands-on experience without relying solely on cadavers or simulations.
Production of Medical Tools and Equipment
3D printing accelerates the production of medical tools and devices. Traditionally, manufacturing surgical instruments involves lengthy processes and high costs. With 3D printing, tools are produced faster and at a fraction of the cost.
For example, customized surgical guides are designed to align perfectly with a patient’s anatomy. These guides enhance the accuracy of surgeries, particularly in orthopedic and dental procedures.
Additionally, during the COVID-19 pandemic, 3D printing addressed shortages of personal protective equipment (PPE) and ventilator components. This flexibility demonstrates the technology’s potential to adapt quickly to urgent healthcare needs.
Bioprinting: The Next Frontier
Bioprinting, an emerging branch of 3D printing, is paving the way for groundbreaking advancements in healthcare. This technology uses bio-ink made from living cells to create tissues and organs. Although still in its early stages, bioprinting holds immense promise for organ transplantation.
Scientists have successfully printed skin, cartilage, and even small liver tissues. These developments could eventually address the global shortage of donor organs. Patients in need of transplants might receive bioprinted organs tailored to their bodies, reducing rejection risks.
Bioprinting also has applications in drug testing. Researchers test new medications on bioprinted tissues, reducing the need for animal testing and speeding up drug development.
Lowering Costs and Improving Accessibility
Healthcare costs remain a global challenge, but 3D printing offers a solution. By streamlining production and reducing waste, this technology makes medical devices and treatments more affordable.
Custom prosthetics, for example, are often expensive and time-consuming to produce. 3D printing drastically lowers costs while delivering better-fitting devices. This affordability benefits patients in low-income regions, providing them access to life-changing solutions.
Additionally, portable 3D printers allow healthcare providers to produce devices and tools in remote areas. This capability ensures timely care, even in regions with limited medical infrastructure.
Challenges and Future Potential
Despite its transformative impact, 3D printing in healthcare faces challenges. Regulatory approval processes are lengthy and complex. Ensuring the safety and reliability of 3D-printed devices is critical.
Moreover, the technology requires skilled professionals and expensive equipment, limiting its accessibility in some regions. However, as advancements continue and costs decline, 3D printing is expected to become more widespread.
The future of 3D printing in healthcare is promising. As bioprinting matures and regulatory barriers ease, its impact will expand further. From custom implants to life-saving organ transplants, the possibilities are endless.
Conclusion
3D printing revolutionizes healthcare by enabling customization, improving surgical outcomes, and advancing medical research. Its applications, from prosthetics to bioprinting, are reshaping the industry and enhancing patient care.
As the technology evolves, 3D printing’s potential continues to grow. It represents a future where healthcare is faster, more accessible, and tailored to individual needs. Embracing this innovation ensures a brighter, healthier tomorrow.