How 3D Printing Is Transforming Healthcare
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, has already made significant strides in various industries. However, its impact on healthcare is particularly groundbreaking. The ability to create customized, precise, and complex structures with 3D printing technology is transforming healthcare in ways that were once thought impossible. From personalized prosthetics to bioprinting tissues and organs, 3D printing is not only improving patient outcomes but also reducing costs and enhancing medical procedures.
Here’s a closer look at how 3D printing is revolutionizing the healthcare industry.
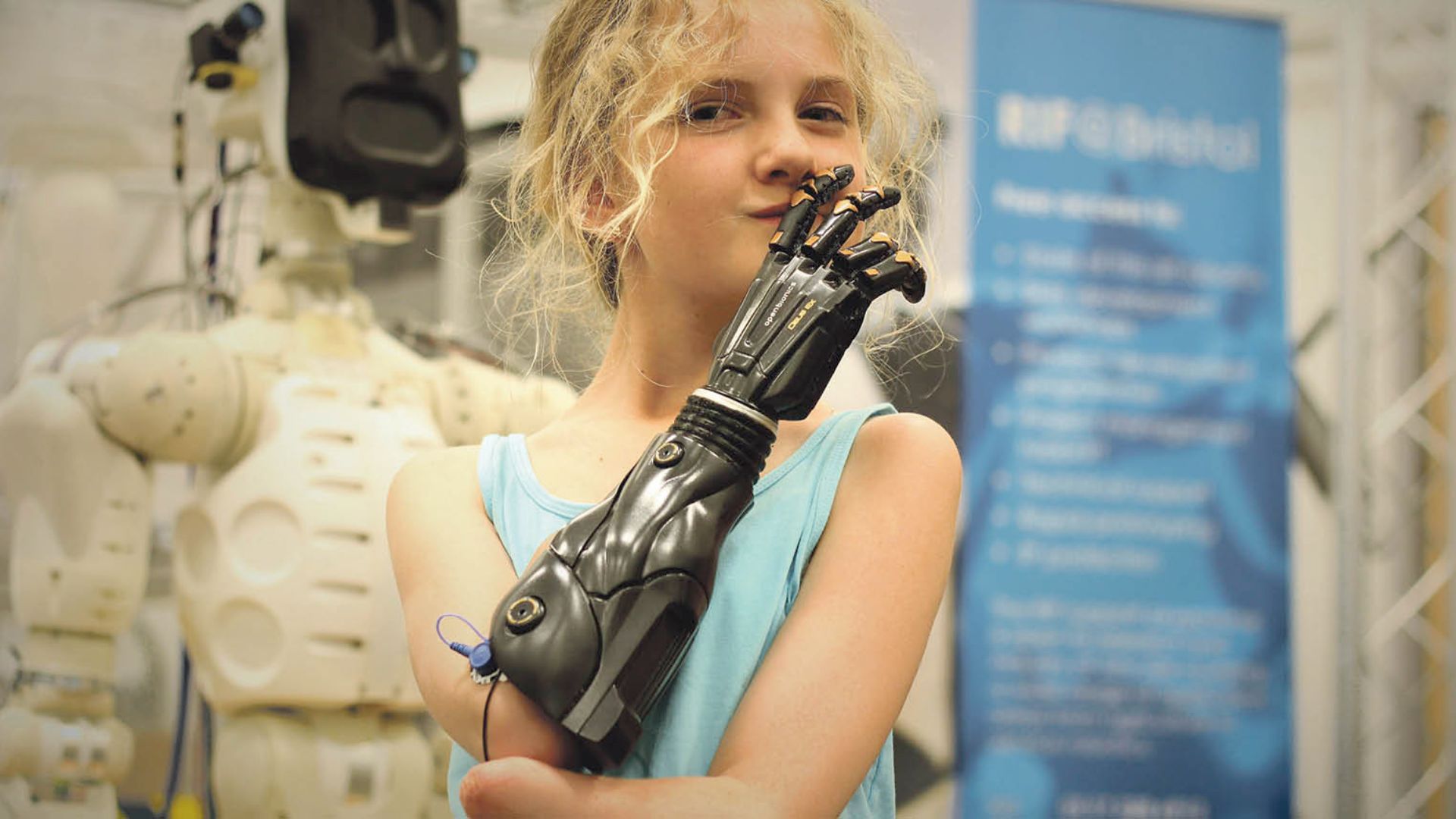
Customized Prosthetics and Implants
One of the most prominent uses of 3D printing in healthcare is in the production of custom prosthetics and implants. Traditional prosthetics are often one-size-fits-all, which can lead to discomfort and suboptimal functionality for patients. With 3D printing, prosthetics and implants can be tailored to an individual’s exact measurements, ensuring a perfect fit and improved comfort.
- Prosthetics: 3D printing allows for the creation of lightweight, functional prosthetics that are designed to meet the unique needs of the patient, improving both usability and aesthetic appeal.
- Implants: Similarly, custom-made implants can be created to fit a patient’s anatomy, whether for dental procedures, joint replacements, or even complex skull surgeries.
This level of personalization has already helped countless patients recover more effectively and lead more fulfilling lives, with fewer complications.
Bioprinting: Printing Organs and Tissues
Perhaps the most futuristic application of 3D printing in healthcare is bioprinting—the process of creating human tissues and organs using a patient’s own cells. While we’re not yet printing entire organs for transplantation, significant progress is being made in the field. Researchers are already using 3D printers to create tissue samples for medical research, drug testing, and even regenerative treatments.
- Printing Tissues: Scientists are using bioprinting to create tissues such as skin, cartilage, and muscle, which could one day be used for grafts or even to repair damaged organs.
- Organ Transplants: Though still in the experimental phase, bioprinting has the potential to create functional organs like kidneys or hearts. This could reduce waiting lists for organ transplants and eliminate the risk of organ rejection by using a patient’s own cells.
While we are still a few years away from fully functional organs, bioprinting could one day eliminate organ shortages and provide life-saving treatments on demand.
Surgical Planning and Models
Another area where 3D printing is making a difference is in surgical planning. Surgeons often rely on 2D images from CT scans or MRIs to plan complex surgeries, but these images don’t always provide the level of detail needed to understand the complexity of the patient’s condition. With 3D printing, surgeons can create physical models of a patient’s anatomy, allowing them to better visualize the problem and plan the surgery with greater precision.
- Preoperative Models: 3D printed models can be made from a patient’s scans, giving surgeons a detailed, hands-on understanding of the affected area before entering the operating room.
- Surgical Training: 3D models can also be used for medical education and training, allowing students and professionals to practice procedures on accurate, life-like models.
This ability to visualize complex anatomy and practice procedures before performing them in real life can lead to better surgical outcomes and faster recovery times.
Personalized Medications
3D printing is also paving the way for personalized medicine, particularly when it comes to medications. One of the most exciting developments is the creation of 3D printed pills that can be customized to release medication at specific times or in specific amounts. This can significantly improve patient outcomes, especially for those with chronic conditions or complex treatment regimens.
- Custom Doses: Doctors could prescribe medications in custom dosages that are tailored to an individual’s needs, improving the efficacy of treatments.
- Targeted Release: With 3D printing, medications can be designed to release their active ingredients at certain times, improving how the body absorbs and utilizes the medication.
This customization could greatly reduce side effects and improve the effectiveness of treatments for a wide range of conditions.
Conclusion
3D printing is undoubtedly transforming healthcare by personalizing treatments, improving surgical precision, and offering innovative solutions to complex medical problems. From creating custom prosthetics and implants to printing tissues and organs, the possibilities of 3D printing in healthcare are limitless. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more groundbreaking innovations that will improve patient care, reduce costs, and lead to better outcomes across the medical field. The future of healthcare is being shaped by 3D printing, and it’s only just beginning.



