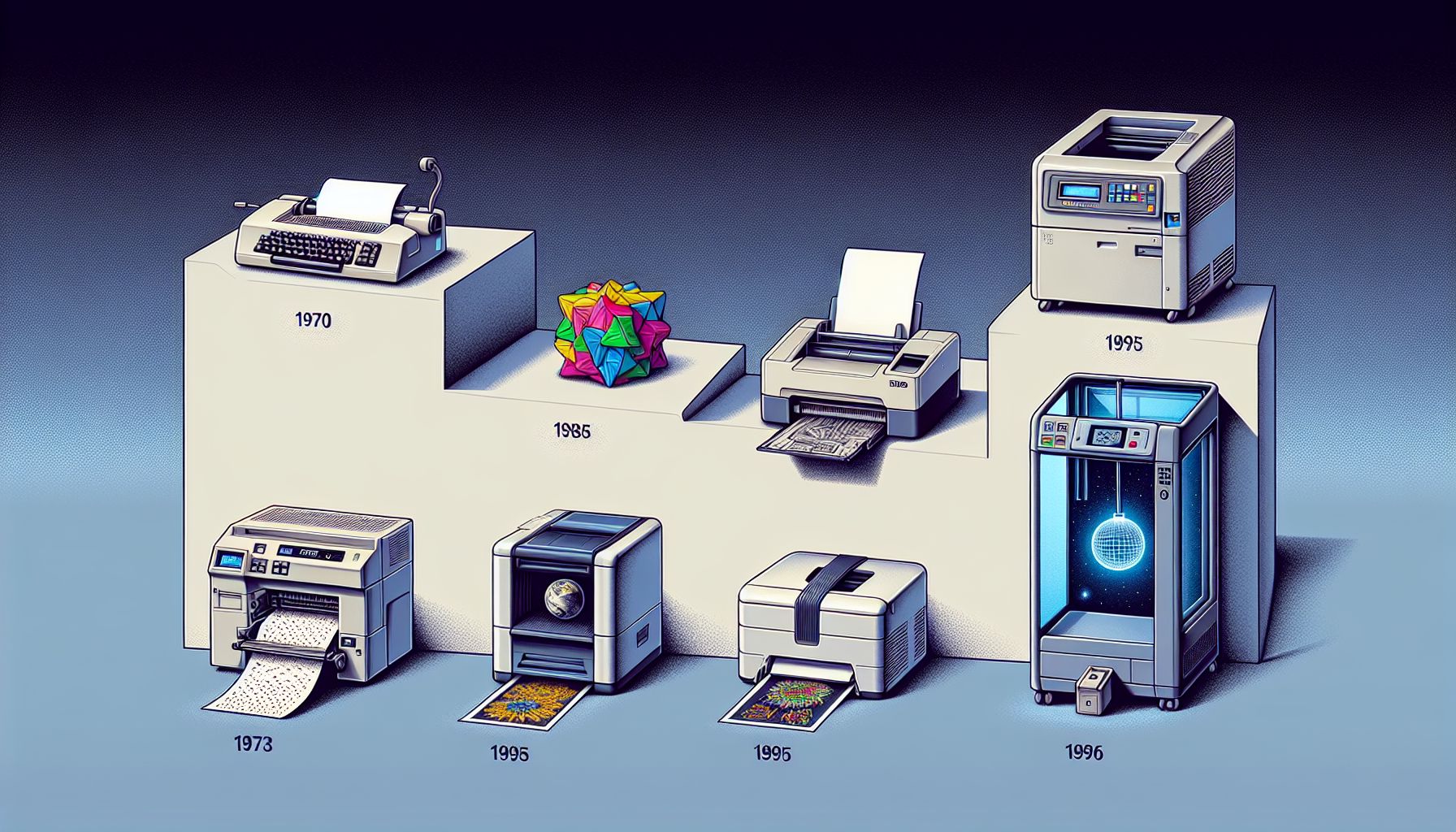
Printers: From Dot Matrix to Wireless Models
Printers have come a long way since their inception, transforming from mechanical machines that produced low-quality prints to sophisticated devices that can deliver high-quality, wireless outputs with the touch of a button. This evolution has greatly impacted how we work, communicate, and access information. In this article, we’ll explore the journey of printers, from the early days of dot matrix technology to the advanced wireless printers we use today.
1. The Early Days: Dot Matrix Printers
The history of printers dates back to the 1950s when dot matrix printers emerged as one of the first commercial printing solutions. These early printers used a print head with pins that struck an inked ribbon, transferring dots onto paper to form characters and images. While dot matrix printers were reliable and cost-effective, the print quality was relatively poor compared to what we’re accustomed to today. They were commonly used for business forms, invoices, and reports.
Despite their limitations in quality, dot matrix printers were instrumental in laying the foundation for modern printing technology. Their ability to print multi-part forms, like carbon copies, made them a popular choice in industrial and office settings.
2. Inkjet Printers: Advancing Print Quality
In the 1980s, inkjet printers revolutionized the printing industry. These printers used tiny nozzles to spray ink onto paper, allowing for much finer and more accurate print quality than dot matrix machines. Inkjet printers became widely used by both individuals and businesses due to their ability to produce high-resolution color prints at relatively affordable prices. They were perfect for printing photographs, promotional materials, and high-quality documents, and quickly gained popularity in home offices and creative fields like graphic design and photography.
As inkjet technology advanced, manufacturers introduced color ink cartridges, further improving print output. The development of multi-functional inkjet printers, which combined printing, scanning, and copying capabilities, added even more versatility, making these printers a staple in both home and office environments.
3. Laser Printers: Speed and Efficiency
Laser printers made their debut in the 1970s and have since become a cornerstone of modern office environments. Unlike inkjet printers, which use liquid ink, laser printers use toner (powdered ink) and a laser beam to produce high-quality text and graphics. Laser printers are known for their speed and efficiency, printing hundreds of pages per minute with high precision.
One of the most significant advantages of laser printers over inkjets is their ability to handle large volumes of printing. Their cost per page is lower, making them ideal for businesses with high-volume printing needs. Laser printers are also capable of producing sharp, crisp text, which is why they remain the go-to choice for printing professional documents.
4. The Rise of Wireless Printers
As the world became more connected through the internet and smart devices, wireless printing emerged as a game-changer. Wireless printers allow users to print from laptops, smartphones, and tablets without needing to connect via cables. Wi-Fi-enabled printers, Bluetooth printers, and cloud-based solutions have made printing more flexible and accessible. With wireless technology, users can print documents from virtually anywhere within the same network or even from remote locations through cloud services like Google Cloud Print or Apple AirPrint.
Wireless printing also brought the convenience of mobile printing, allowing users to send print jobs directly from their mobile devices. Whether in an office or at home, wireless printers provide the ultimate convenience, eliminating the hassle of connecting cables and offering greater mobility.
5. The Future: 3D Printing and Smart Printers
As technology continues to evolve, printers have advanced beyond traditional 2D printing. One of the most exciting developments is 3D printing, which has transformed manufacturing, healthcare, and design industries. 3D printers use digital models to create three-dimensional objects layer by layer. This technology has opened up new possibilities for prototyping, product design, medical implants, and even food printing.
Moreover, smart printers are now on the rise, integrating artificial intelligence (AI) and automation into the printing process. These printers can monitor ink levels, diagnose issues, and even reorder supplies automatically. Some smart printers can adjust print settings based on the content being printed, optimizing print quality and efficiency.
Conclusion
The evolution of printers from dot matrix to wireless and smart models highlights how technology has transformed the way we print and interact with documents. What started as a simple mechanical device for printing basic text has evolved into a sophisticated tool capable of producing high-quality, efficient, and versatile outputs. As new technologies like 3D printing and smart printers emerge, we can expect even more innovation and convenience in the printing industry in the years to come.



