The Evolution of Printing Technology Over the Decades
The history of printing technology dates back to ancient civilizations, but it wasn’t until the 15th century that the invention of the printing press revolutionized the world. Early printing methods were slow and labor-intensive, but they paved the way for the advanced technologies we use today. Over the centuries, printing has evolved, bringing changes to how we create, distribute, and access information. Here’s a look at how printing technology has transformed over the decades.
The Invention of the Printing Press (1440s)
The first major breakthrough in printing came with Johannes Gutenberg’s invention of the movable type printing press in the mid-15th century. This innovation allowed for the mass production of books and written materials, making them more accessible to the public. Before the printing press, books were painstakingly handwritten, a time-consuming and costly process. Gutenberg’s press changed all that, allowing for quicker, more efficient printing that led to the spread of knowledge during the Renaissance.
The Rise of Lithography (Late 1700s – Early 1800s)
In the late 18th century, lithography was developed by Alois Senefelder, marking a significant advancement in printing technology. Lithography enabled the printing of images and text from a flat surface, making it more suitable for high-volume print jobs like posters, newspapers, and books. This process paved the way for the mass production of color images, something that was previously impossible or extremely expensive. By the 19th century, lithography became widely used in the publishing and advertising industries.
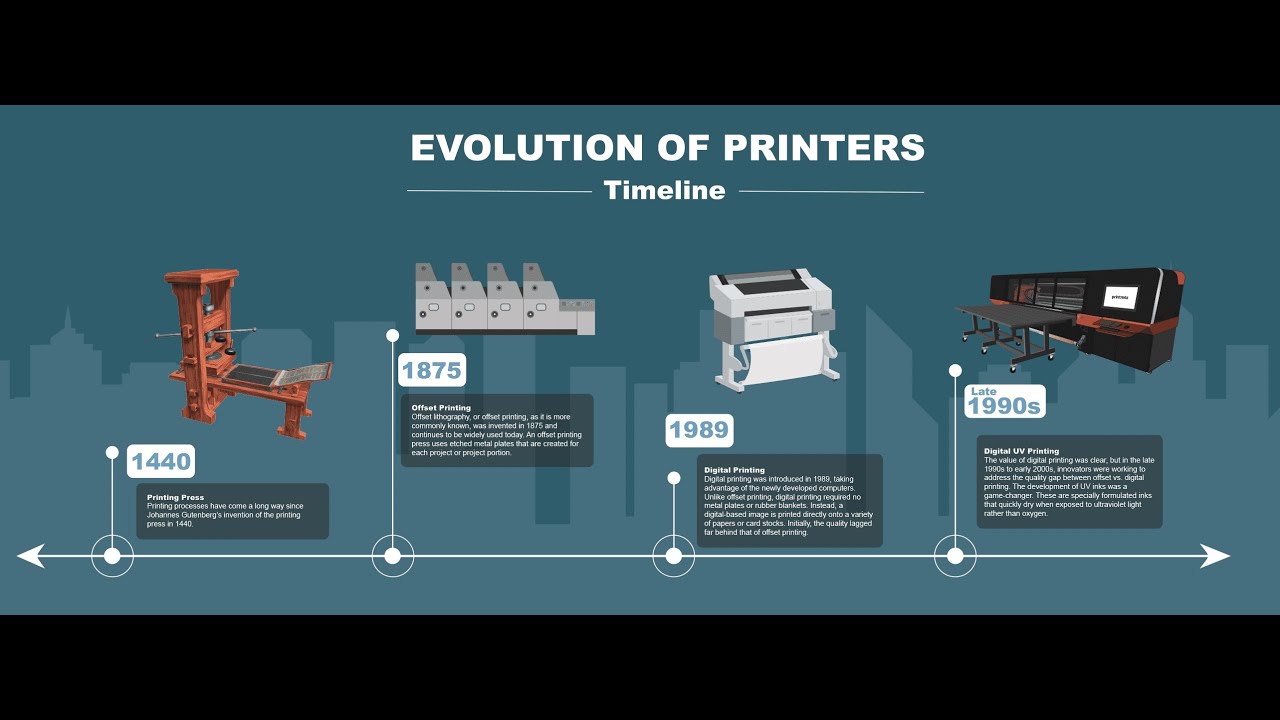
The Advent of Offset Printing (Early 1900s)
Offset printing emerged in the early 20th century as a significant improvement to lithography. This process involves transferring ink from a metal plate to a rubber blanket before applying it to the printing surface. The offset method allowed for faster production speeds, improved image quality, and better cost efficiency. This innovation played a crucial role in the printing of newspapers, magazines, and books, furthering the reach of mass media during the 20th century.
The Digital Revolution and the Birth of Inkjet and Laser Printers (1970s – 1980s)
The 1970s and 1980s marked a major shift in the printing industry with the development of digital printing technologies. Inkjet printers, first introduced by companies like Epson and Canon, used liquid ink to create images and text by spraying tiny droplets onto paper. Laser printers, developed by Xerox and later other manufacturers, used a laser beam to transfer toner onto paper in a high-speed process. These printers revolutionized home and office printing by providing a more affordable, convenient, and efficient way to print documents compared to older technologies.
The Growth of Color Printing (1990s)
In the 1990s, color printing technology became more widely available, especially in inkjet printers. Early color printers were expensive and often had slow printing speeds, but over time, advancements in technology led to faster, more affordable options. The introduction of high-quality color printing made it possible for businesses and individuals to print marketing materials, photographs, and other color-rich documents from the comfort of their own homes or offices. This period marked the democratization of professional-quality printing.
The Rise of 3D Printing (2000s – Present)
While traditional printing methods focused on producing two-dimensional images and text, the 21st century brought the revolutionary concept of 3D printing. The early 2000s saw the development of 3D printing technologies that could print physical objects from digital models. Using materials like plastic, metal, and even biological tissue, 3D printing has transformed industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, architecture, and fashion. The technology has made rapid prototyping and custom manufacturing more accessible and cost-effective, heralding a new era in industrial and personal printing.
Cloud Printing and Mobile Printing (2010s – Present)
The last decade has seen the rise of cloud-based and mobile printing solutions. With the increasing reliance on smartphones, tablets, and cloud storage, printing from anywhere has become a reality. Cloud printing allows users to send documents to a printer over the internet, eliminating the need for direct connections to the device. Mobile printing, available through apps like Apple AirPrint and Google Cloud Print, allows users to print from their mobile devices to any compatible printer, even when they are far from their office or home. These advancements have further simplified and streamlined the printing process, making it easier to print on the go.
Sustainable Printing Practices (2010s – Present)
As environmental concerns grow, the printing industry has shifted toward more sustainable practices. The development of eco-friendly printers, as well as ink and toner cartridges that use less waste and energy, has been a key focus. Many companies are now offering recycling programs for used cartridges, and digital printing technologies are minimizing paper waste by offering precise, on-demand printing. Additionally, technologies like duplex printing (printing on both sides of the paper) help reduce paper consumption, contributing to greener, more sustainable printing practices.
Conclusion
The evolution of printing technology over the decades has drastically transformed the way we produce and consume information. From the invention of the printing press to the rise of digital, 3D, and mobile printing, each advancement has contributed to making printing faster, more efficient, and more accessible. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more innovations in printing that will impact industries ranging from education and publishing to manufacturing and healthcare. The future of printing is bound to be as exciting and transformative as its past.



